The sugar packaging industry stands at a critical juncture where traditional challenges meet modern demands for sustainability, efficiency, and compliance. With the global sugar packaging market reaching significant scale and flexible packaging expected to grow at 4.7% CAGR through 2034, manufacturers face mounting pressure to optimize their packaging lines while meeting evolving regulatory requirements and consumer expectations.

This comprehensive guide addresses five core challenges that define sugar packaging success: preventing moisture-related product degradation, achieving cost-effective automation, implementing sustainable materials and processes, ensuring quality control and traceability, and preparing for emerging 2026 trends. Whether you’re managing high-volume production lines or evaluating packaging format transitions, the solutions outlined here provide actionable pathways to enhanced efficiency, reduced costs, and improved market positioning.
Who This Guide Is For
Sugar manufacturers, packaging engineers, and operations managers face a complex landscape of competing priorities. Production facilities processing granulated, powdered, or specialty sugars must balance speed requirements with quality standards while navigating sustainability mandates and cost pressures.
Small to medium enterprises typically struggle with 30-80 packages per minute capacity constraints and limited flexibility for SKU changes, while large-scale operations demand 250+ packages per minute throughput with minimal downtime. Both segments share common pain points: moisture intrusion leading to clumping and quality degradation, excessive packaging material costs, regulatory compliance complexity, and difficulty achieving consistent seal integrity across varied environmental conditions.
The solutions presented address these challenges through data-driven equipment selection, material optimization, and process improvements that have demonstrated measurable results across diverse operational scales. From bulk storage operations requiring food-grade buckets with gamma lids to high-speed consumer packaging lines demanding advanced VFFS technology, this guide covers the spectrum of sugar packaging needs.
Your Core Packaging Challenges
Moisture Control and Product Integrity
Sugar’s hygroscopic nature creates persistent quality control challenges, with moisture absorption rates varying significantly based on packaging barrier performance. As one industry expert notes: “Sugar is pretty easy to store. It basically needs to be kept dry and away from anything with an odor, as it will take on that smell.” This simple principle underlies complex technical requirements for commercial packaging operations.
Research demonstrates that uncoated OPP films allow moisture transmission rates exceeding 67.0 g mm/m²·d·bar, while high-barrier PVdC coatings reduce this by 10-40% depending on film thickness. Advanced multilayer structures incorporating modified PVOH barriers achieve moisture transmission rates as low as 3.5 g mm/m²·d·bar under controlled humidity conditions. For long-term storage applications, operators report success with mylar bags sealed without oxygen absorbers, achieving 25-year storage life when properly implemented.
The economic impact of moisture control extends beyond product quality to encompass customer returns, production waste, and brand reputation damage. Facilities experiencing frequent clumping issues report 3-8% product loss rates and increased customer complaint volumes, translating to substantial revenue impact across high-volume operations. Professional storage solutions incorporate desiccant packs and proper container selection, with food-grade buckets and gamma lids providing reliable moisture barriers for bulk applications.
Production Efficiency and Cost Control
Manual packaging operations typically achieve 30-50 packages per hour per operator, with labor costs comprising 40-60% of total packaging expenses. Automated systems demonstrate 25-40% labor cost reduction while increasing throughput to 60-300+ packages per minute depending on technology selection. The payback period for automation investments commonly ranges from 12-24 months, with faster returns achievable in high-volume environments.
Material utilization efficiency represents another significant cost factor, with flexible packaging formats using approximately 70% less material than rigid alternatives. This reduction directly impacts per-unit costs while supporting sustainability objectives and transportation efficiency improvements. Businesses implementing automated packaging report efficiency boosts of up to 50%, with consistent quality and reduced waste further enhancing cost-effectiveness.
The choice between packaging technologies significantly impacts operational efficiency. VFFS machines excel in high-speed production environments, forming bags from continuous film rolls while filling and sealing in one process. This automation reduces labor requirements while enabling rapid production speeds suitable for large-scale operations. HFFS machines offer horizontal processing ideal for sachets and portion packs, providing precision filling and customization capabilities for specialized applications.
Regulatory Compliance and Traceability
Evolving food safety regulations, particularly the FDA’s Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) Final Rule requiring 24-48 hour traceability for recalls by January 2026, create new packaging requirements. The European Union’s Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR) mandates recyclability improvements and material composition transparency, while similar regulations emerging globally create consistent pressure for sustainable packaging transitions.
2D barcode implementation becomes essential for compliance, with GS1 Digital Link standards enabling comprehensive product information storage including batch numbers, expiration dates, and supply chain data. Companies implementing robust traceability systems report 25-35% processing time savings and improved recall response capabilities. Modern coding systems operate at line speeds exceeding 300 packages per minute with 99.9%+ code quality grades ensuring reliable scanning throughout the supply chain.
Food-grade container selection requires careful attention to regulatory compliance, with FDA-approved materials essential for direct food contact applications. Storage operators emphasize the importance of using properly certified food-grade buckets and avoiding direct concrete contact to prevent contamination and moisture accumulation.
Design That Sells and Protects
Barrier Performance Optimization
Effective sugar packaging requires multi-layered approach to moisture protection, combining appropriate material selection with proper seal integrity. High-performance barrier films incorporating SiOx coatings achieve oxygen transmission rates below 1.0 cm³/m²·day and water vapor transmission rates under 1.5 g/m²·day, providing extended shelf life protection even in challenging humidity environments.
Professional storage operations utilize mylar bags for long-term preservation, with operators reporting successful 25-year storage without oxygen absorbers when properly sealed. The selection between laminated structures and coated films depends on specific product requirements and cost constraints. Laminated PE/paper combinations offer good moisture resistance at competitive costs, while specialized barrier films with PVdC or EVOH layers provide superior protection for premium products or extended distribution chains.
Package format selection significantly impacts barrier effectiveness, with stand-up pouches and gusseted bags providing improved moisture protection compared to traditional pillow bags due to reduced seal length exposure and enhanced structural integrity during handling. For bulk storage applications, vacuum-sealed glass jars with proper attachments offer excellent long-term preservation, particularly when combined with appropriate oxygen absorbers.
Visual Appeal and Consumer Convenience
Modern sugar packaging must balance protective performance with shelf appeal and consumer convenience. Packaging serves multiple functions beyond mere protection: it communicates brand values, influences consumer perception, and affects purchasing decisions. A well-designed package acts as a silent salesperson, differentiating products in crowded markets while building brand loyalty.
Flexible packaging formats enable high-quality printing and finishing options while maintaining cost efficiency, with digital printing technologies supporting smaller batch runs and rapid SKU changes without cylinder investments. Clear window options and transparent materials allow product visibility while maintaining barrier properties through strategic lamination techniques.
Convenience features increasingly drive consumer preference, with resealable packaging offering enhanced product preservation after opening. Resealable pouches and zipper bags provide practical solutions that reduce waste while maintaining freshness. Multi-compartment packaging designs cater to diverse consumer needs, offering variety and portion control in single packages. Stick pack machines produce convenient single-serving formats ideal for on-the-go consumption and hospitality applications.
Brand differentiation increasingly depends on sustainable messaging and transparent labeling, with 77% of consumers considering product information important in purchase decisions and 79% preferring products with scannable codes providing detailed information.
Automation That Fits Your Volume
VFFS vs Premade Pouch Decision Framework
Vertical Form Fill Seal (VFFS) machines excel in high-speed, consistent production environments, typically achieving 150-300 bags per minute with granulated sugar applications. These systems demonstrate superior material efficiency through continuous film usage and integrated sealing processes, resulting in lower per-unit packaging costs for large-volume production. VFFS machines form bags from film rolls, fill with product, and seal in one continuous process, maximizing automation benefits while minimizing labor requirements.
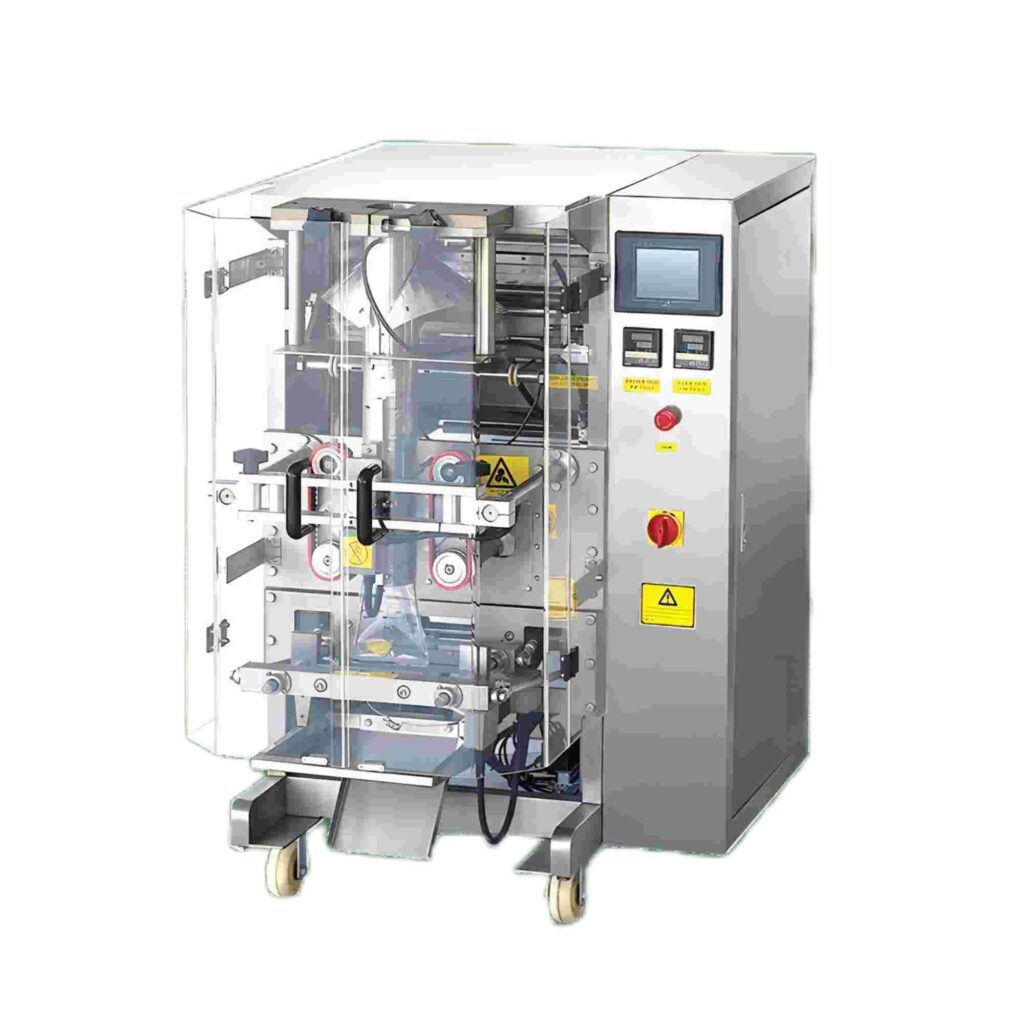

VFFS advantages include compact footprint requirements, consistent bag dimensions, and reduced material waste through optimized film usage. However, these systems require skilled operators for setup and maintenance, with changeover times of 30-60 minutes for different bag sizes representing potential efficiency constraints for multi-SKU operations.
Premade pouch packaging machines offer enhanced flexibility and visual appeal, supporting diverse bag styles including stand-up pouches, zipper closures, and specialty formats. Production speeds typically range from 60-120 bags per minute, with significantly faster changeover capabilities (10-20 minutes) making them ideal for facilities with frequent product switches or smaller batch requirements.
Horizontal Form Fill Seal (HFFS) machines provide specialized solutions for sachets and flat packets, offering precision filling and customization capabilities. These machines excel in portion control applications, producing the small, convenient packets commonly used in food service environments.
The decision framework should consider production volume, SKU variety, operator skill availability, and quality requirements. VFFS systems prove most cost-effective above 1,000 bags per hour sustained production, while premade pouch machines excel for operations below this threshold or requiring premium packaging aesthetics.
Equipment Selection and ROI Analysis
Automation investment analysis requires comprehensive evaluation of labor cost savings, material efficiency improvements, quality enhancement benefits, and throughput increases. Labor cost reduction typically ranges from 25-40% for automated systems, with additional savings from reduced product waste and improved consistency. Automated packaging can boost overall efficiency by 50% while ensuring consistent quality standards.

Stick pack machines offer specialized solutions for single-serving applications, producing slim, tubular packages ideal for portable consumption. These machines cater to growing consumer demand for convenience and portion control, particularly in hospitality and retail environments. Sachet packing machines provide cost-effective solutions for small, flat packets commonly used in food service applications.
Material cost optimization through automated systems includes reduced film waste (2-5% improvement), consistent fill weights (±0.5% accuracy versus ±2% manual), and optimized seal parameters reducing rejects. These improvements compound over high-volume production to generate substantial annual savings.
For bulk operations, specialized heavy-duty systems handle large bags and totes efficiently, optimizing logistics while reducing packaging waste. These systems support manufacturers and distributors requiring cost-effective solutions for large-volume operations.
Implementation timeline typically spans 10-16 weeks from equipment selection to full production, including installation, training, and process optimization. Successful implementations require dedicated project management, operator training programs, and systematic performance monitoring during ramp-up phases.
Sustainability That Pays Back
Eco-Friendly Materials and Environmental Impact
The sustainable packaging market, valued at $292.71 billion in 2024 and projected to reach $423.56 billion by 2029, reflects growing regulatory and consumer pressure for environmental responsibility. Sugar packaging manufacturers implementing sustainable materials report both cost savings and enhanced brand positioning. With growing environmental concerns, businesses increasingly switch to biodegradable or recyclable materials to reduce carbon footprint and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
Mono-material packaging structures, particularly mono-PE and kraft/PE laminates, enable full recyclability in most municipal systems while maintaining adequate barrier properties for sugar applications. Post-consumer recycled (PCR) content incorporation, targeting 15-30% by weight, supports circular economy principles while meeting extended producer responsibility (EPR) requirements.
Carbon footprint reduction strategies focus on material optimization, manufacturing efficiency, and transportation improvements. Flexible packaging typically generates 70% lower carbon emissions compared to rigid alternatives through reduced material usage and improved shipping efficiency. Companies implementing comprehensive sustainability programs report 13-15% GHG emission reductions across their value chains.
Smart packaging technology integrates digital elements into design, including QR codes providing product information and augmented reality experiences. This technology transforms packaging into interactive platforms, enhancing customer engagement while providing valuable consumer behavior insights. Digital integration also improves supply chain transparency, offering real-time tracking and authenticity data.
Regulatory Compliance and Future-Proofing
The European Union’s PPWR regulation mandates packaging recyclability by 2030 with interim targets beginning in 2026. Compliance requires mono-material designs, clear recycling instructions, and material composition documentation. Similar regulations emerging globally create consistent pressure for sustainable packaging transitions, making early adoption strategically advantageous.
Extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs increasingly tie packaging fees to environmental impact, making sustainable material choices financially advantageous. Companies utilizing high recycled content and recyclable structures experience lower EPR fees, creating direct cost benefits beyond sustainability messaging.
Carbon-negative packaging technologies, while currently niche, represent emerging opportunities for differentiation. The carbon-negative packaging market demonstrates significant growth potential as manufacturing processes and material technologies advance to support net-positive environmental impacts.
Custom packaging designs allow businesses to differentiate products while incorporating sustainability features. Unique, visually appealing designs strengthen brand identity while supporting environmental objectives through material selection and design optimization. This approach balances marketing needs with sustainability goals, creating comprehensive competitive advantages.
QC and Traceability, Built In
Automated Quality Control Systems
Modern sugar packaging lines integrate multiple quality control technologies ensuring consistent seal integrity, accurate fill weights, and proper labeling. In-line weighing systems achieve ±0.1g accuracy at production speeds exceeding 200 packages per minute, with automatic reject systems maintaining quality standards without operator intervention.
Vision inspection systems monitor seal quality, detecting incomplete seals, wrinkles, and contamination that could compromise product integrity. These systems typically identify defects with 99.5%+ accuracy while operating at full line speeds, preventing quality issues from reaching distribution channels. Proper quality control becomes particularly important for sugar products due to moisture sensitivity and clumping risks.
Metal detection and foreign object removal systems protect product safety and brand reputation. Advanced systems distinguish between product and contamination with minimal false positives, maintaining production efficiency while ensuring consumer safety compliance. For storage operations, pest control measures including freezing product for 24-48 hours before packaging eliminate potential contamination risks.
Temperature and humidity monitoring throughout packaging operations ensure optimal conditions for product preservation. Environmental controls prevent moisture accumulation during processing while maintaining product quality standards. Proper storage facilities avoid direct concrete contact and implement moisture barriers to prevent contamination during storage periods.
2D Barcode Implementation and Benefits
2D barcode technology enables comprehensive traceability data storage in compact, scannable formats suitable for high-speed packaging lines. QR codes and Data Matrix formats support batch numbers, production dates, facility identification, and supply chain routing information required for FSMA compliance. Implementation addresses growing regulatory requirements while providing consumer engagement opportunities.

Modern coding systems integrate seamlessly with production management systems, enabling real-time data capture and automatic code generation. These systems operate at line speeds exceeding 300 packages per minute with 99.9%+ code quality grades ensuring reliable scanning throughout the supply chain. Advanced coding capabilities support complex data structures including GS1 Digital Link standards.
The business case for 2D barcode implementation includes improved recall response capabilities, reduced manual tracking requirements, and enhanced consumer engagement opportunities. Companies report 25-35% processing time savings and improved supply chain visibility following implementation. Traceability systems also support inventory management and loss prevention initiatives across distribution networks.
Smart packaging integration enables direct consumer interaction through enhanced QR codes, providing recipe suggestions, sustainability information, and brand storytelling opportunities. This technology creates value-added consumer experiences while supporting marketing and customer engagement objectives.
Future Trends 2026: Smart Packaging Evolution
Intelligent Packaging Technologies
Smart packaging integration represents a significant trend for 2026, with temperature-sensitive indicators, freshness sensors, and interactive consumer engagement features becoming commercially viable for sugar applications. These technologies support both quality assurance and marketing differentiation strategies while providing real-time product condition monitoring.
Near-field communication (NFC) and enhanced QR codes enable direct consumer interaction, providing recipe suggestions, sustainability information, and brand storytelling opportunities. Implementation costs have decreased sufficiently to support mass-market adoption across diverse product categories. Interactive packaging transforms traditional containers into engagement platforms, building stronger consumer relationships.
Predictive maintenance systems using IoT sensors and machine learning algorithms optimize packaging line performance, predicting maintenance requirements and minimizing unplanned downtime. These systems typically reduce maintenance costs by 15-25% while improving overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). Advanced analytics identify performance trends and recommend optimization strategies before issues impact production.
Augmented reality integration creates immersive consumer experiences, allowing virtual product demonstrations and enhanced information delivery. This technology particularly benefits premium product segments where consumer education and engagement drive purchasing decisions.
Circular Economy Integration
Packaging design increasingly prioritizes end-of-life considerations, with chemical recycling technologies enabling closed-loop material flows for complex laminated structures. Advanced recycling processes can handle previously non-recyclable flexible packaging, expanding material recovery options while supporting circular economy principles.
Bio-based barrier materials derived from renewable sources offer improved sustainability profiles while maintaining performance characteristics required for sugar packaging. These materials, while currently premium-priced, demonstrate cost improvement trends supporting broader adoption by 2026. Innovation in bio-based materials creates opportunities for sustainable differentiation while meeting regulatory requirements.
Refillable packaging formats and concentrated product options align with consumer preferences for reduced environmental impact. Bulk packaging systems for foodservice and industrial applications support circular economy principles while reducing per-unit packaging costs. Reusable container programs create customer loyalty while supporting sustainability objectives.
Multi-compartment packaging innovations provide variety and portion control in single packages, reducing overall packaging requirements while enhancing consumer convenience. These designs optimize material usage while creating premium product positioning opportunities.
Supply Chain Digitization
Blockchain integration with packaging traceability systems creates immutable supply chain records, supporting authenticity verification and enhanced food safety protocols. Implementation complexity has decreased through standardized platforms and improved system integration capabilities, making adoption feasible for medium-scale operations.
Automated packaging line monitoring using advanced analytics enables real-time optimization and predictive quality control. These systems analyze production data to identify trend patterns and recommend adjustments before quality issues develop. Machine learning algorithms continuously improve performance recommendations based on historical data and production conditions.
Digital twin technology for packaging operations enables virtual optimization and training scenarios, reducing implementation risks and accelerating operator competency development. This technology particularly benefits complex automated systems requiring specialized operating knowledge while supporting continuous improvement initiatives.
Supply chain transparency increases through integrated tracking systems, providing consumers and regulators with comprehensive product journey documentation. This transparency supports premium positioning while meeting evolving regulatory requirements for food safety and authenticity verification.
Conclusion: Make Your Decision
Successful sugar packaging optimization requires systematic evaluation of production requirements, quality standards, sustainability objectives, and market positioning goals. The integration of appropriate automation technology, sustainable materials, and advanced quality control systems creates competitive advantages while managing operational costs effectively.
The decision sequence should prioritize immediate operational challenges while building flexibility for future requirements. High-volume producers benefit most from VFFS automation and integrated quality systems, while smaller operations may achieve better results through premade pouch flexibility and modular equipment approaches. Storage and bulk operations require careful attention to moisture control through proper container selection and environmental management.
Sustainability integration cannot be treated as an afterthought but must be incorporated into fundamental packaging design decisions. The regulatory landscape increasingly favors early adopters of sustainable practices, creating both compliance advantages and cost benefits through EPR fee optimization. Smart packaging technologies provide differentiation opportunities while supporting traceability and consumer engagement objectives.
Equipment selection requires comprehensive analysis of production volume, SKU variety, operator capabilities, and quality requirements. VFFS systems excel above 1,000 packages per hour with consistent production needs, while premade pouch machines provide flexibility for varied applications. Specialized equipment including stick pack and sachet machines serve niche applications with specific performance advantages.
Implementation success depends on comprehensive planning, operator training, and systematic performance monitoring. Companies achieving the best results typically engage experienced packaging consultants during equipment selection and maintain dedicated project management throughout implementation phases. Proper storage techniques, including appropriate container selection and moisture control measures, ensure product quality throughout distribution cycles.
The 2026 packaging landscape will reward manufacturers who balance operational efficiency with sustainability leadership and regulatory compliance. Starting these transformations now enables competitive positioning and operational optimization before market pressures intensify further. Whether implementing advanced automation systems or optimizing storage operations, the key lies in matching solutions to specific operational requirements while building flexibility for future needs.
Do not hesitate to contact us if any question.





